Comprehensive Guide to Concrete Scanning Technologies
Comprehensive Guide to Concrete Scanning Technologies
Blog Article
Introduce the Transformative Power of Concrete Scanning in Making Best Use Of Performance and Security
Concrete scanning has arised as an important device in the building sector, providing unrivaled benefits in improving task efficiency and ensuring safety and security standards. By using innovative technology, concrete scanning enables specialists to see past the surface, discovering surprise complexities that might influence the structural integrity of a structure. The transformative power of concrete scanning hinges on its ability to give real-time information and in-depth insights, revolutionizing how tasks are planned and carried out. As we look into the details of this innovative method, a world of possibilities opens, showcasing a brand-new period of building and construction methods that prioritize precision and protection.
Value of Concrete Scanning
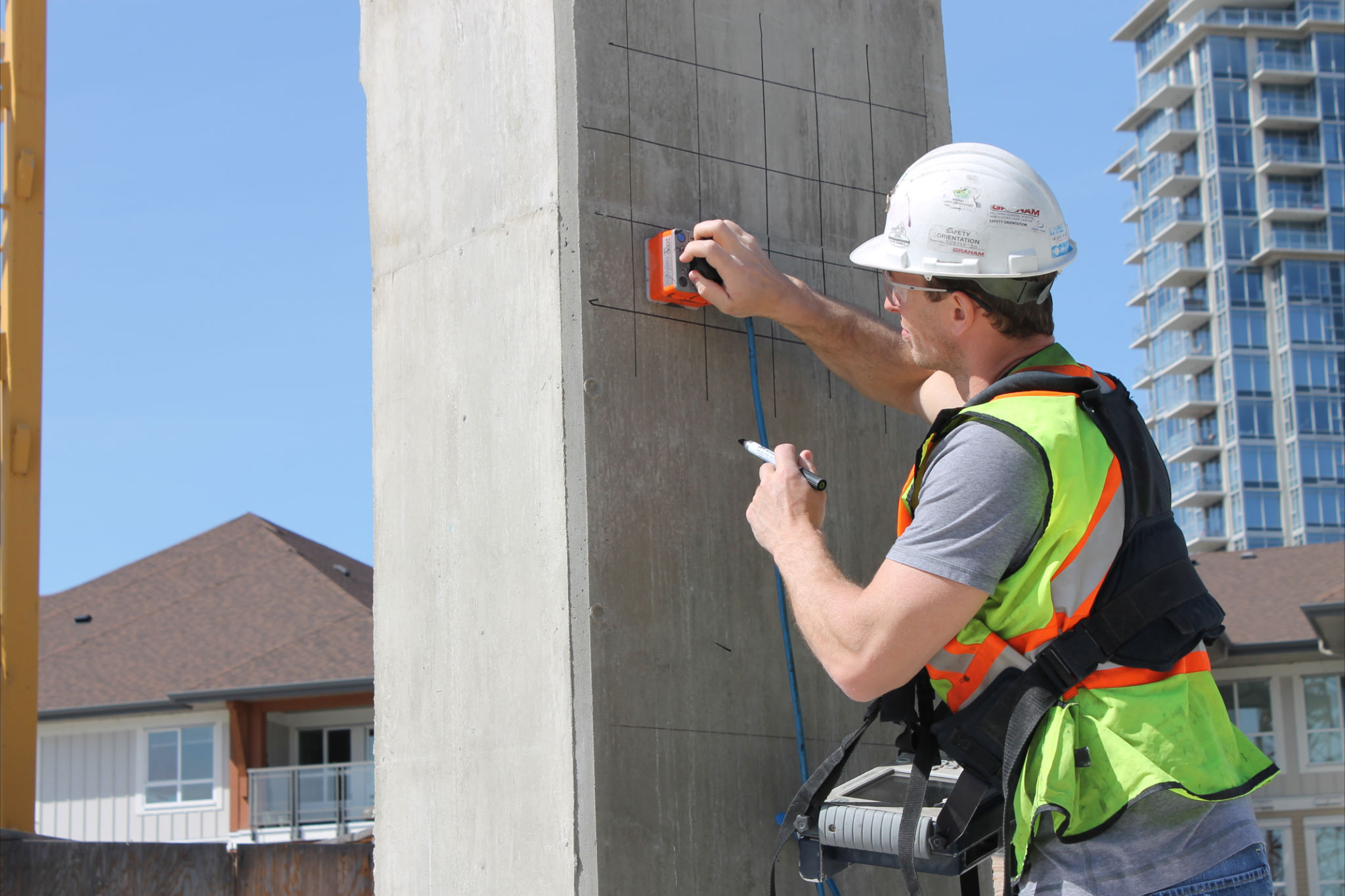
Guaranteeing the structural honesty and security of construction tasks starts with the important step of conducting comprehensive concrete scanning. Concrete scanning is a non-destructive method used to spot and map subsurface aspects within concrete frameworks. This process is crucial in determining potential dangers, such as rebar, post-tension cable televisions, and avenues, that may be concealed within the concrete. By using advanced innovations like ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electromagnetic induction, building and construction groups can accurately locate these elements without creating any type of damages to the framework.
Additionally, concrete scanning helps in enhancing job timelines and budget by avoiding unexpected expenses and hold-ups that might occur due to unpredicted blockages within the concrete. Ultimately, spending in comprehensive concrete scanning is an aggressive method that improves both performance and safety in construction jobs.
Just How Concrete Scanning Functions
Concrete scanning runs as a crucial tool in building and construction projects by using advanced innovations to find and map subsurface elements without causing architectural damage. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) are two main techniques made use of in concrete scanning. GPR jobs by releasing high-frequency radar pulses right into the surface, which get better when they come across subsurface items or gaps. The time taken for the signal to return suggests the deepness and place of the items. EMI, on the other hand, uses electro-magnetic fields to determine variations in product make-ups, such as identifying rebar or avenues within concrete frameworks.
Throughout the scanning process, the information accumulated is examined in real-time, enabling immediate identification of prospective hazards or barriers below the surface area. By using these sophisticated modern technologies, concrete scanning significantly decreases the danger of expensive problems and injuries on building and construction sites.
Benefits of Concrete Scanning
Using sophisticated scanning innovations in building and construction projects uses a multitude of benefits, enhancing both performance and security on-site. Among the primary advantages of concrete scanning is the capacity to spot and locate embedded items such as rebar, post-tension wires, and conduits properly. By identifying these elements prior to drilling or cutting into concrete frameworks, the risk of unexpected strikes is dramatically lowered, stopping prospective injuries to employees and damages to the structure itself. Concrete scanning helps in preparation and developing more properly, as it offers specific info about the area and depth of architectural elements.
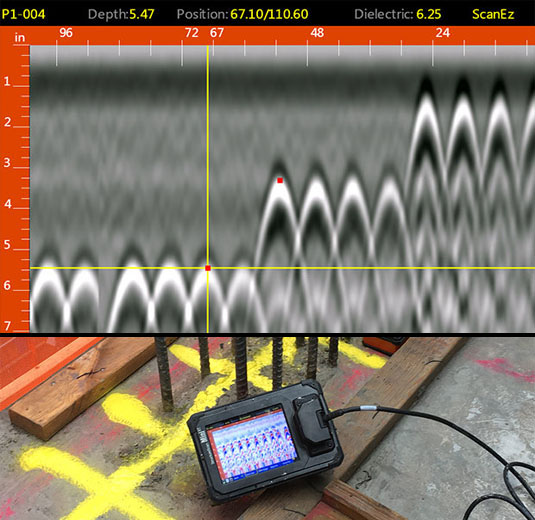
Instance Research Studies: Concrete Scanning Success

In another case, a building and construction company utilized 3D concrete scanning to evaluate the condition of aging concrete structures in a historic building. The comprehensive scans offered valuable understandings right into the extent of degeneration and aided focus on upkeep efforts efficiently. By proactively attending to locations of concern recognized via scanning, the business was able to extend the lifespan of the framework and make certain owner security.
These study underscore the transformative power of concrete scanning in enhancing performance, accuracy, and safety and security in building tasks.
Applying Concrete Scanning in Projects
Implementing sophisticated scanning innovations during building jobs has ended up being progressively necessary for boosting accuracy and safety and security. By incorporating concrete scanning into job preparation and execution, construction groups can recognize prospective threats, such as rebar or post-tension cable televisions, concealed within concrete frameworks. This positive method minimizes the danger of crashes, hold-ups, and costly rework, eventually resulting in extra effective project timelines and budgets.
To execute concrete scanning successfully, task supervisors should team up carefully with seasoned scanning experts to figure out the most appropriate scanning strategies for the specific task needs. Engaging scanning professionals from the early stages of a task makes it possible for the group to develop thorough scanning plans that address key areas of worry and guarantee extensive information collection.
Furthermore, including concrete scanning right into routine project process can streamline decision-making procedures, as real-time check data gives instant understandings right into the condition of concrete structures - Concrete Scanning. This data-driven approach assists in educated analytical and allows teams to make the original source adjustments immediately, cultivating a culture of performance and safety throughout the job lifecycle

Verdict
Finally, concrete scanning plays a critical role in boosting efficiency and safety and here security in building jobs. By utilizing advanced technology to map and spot out underlying structures within concrete, this procedure assists to avoid expensive blunders, ensure structural stability, and lessen threats on site. With the ability to discover concealed elements and supply exact data, concrete scanning confirms to be a useful tool for maximizing task results and taking full advantage of total success.
Concrete scanning is a non-destructive approach made use of to identify and map subsurface components within concrete frameworks. In addition, concrete scanning aids in maximizing job timelines and spending plan by staying clear of unanticipated prices and hold-ups that may develop due to unforeseen obstructions within the concrete. One significant instance study includes a large-scale improvement job where concrete scanning played an important duty in making certain project success.In one more instance, a construction company made use of Continued 3D concrete scanning to analyze the problem of maturing concrete structures in a historic building. By incorporating concrete scanning right into task preparation and implementation, building and construction groups can determine potential threats, such as rebar or post-tension cords, hidden within concrete structures.
Report this page